Probability
- Discrete Probability: Involves a random variable that can only take on a finite or countable number of values
- Continuous Probability: Involves a random variable that can take on any value within a given range
- Prior Probability: An initial probability assigned to an event before any new information is obtained
- Posterior Probability: The updated probability of an event after incorporating new evidence
Linear Algebra
- Linear Algebra: Linear Algebra is the study of vectors and certain rules to manipulate vectors.
- Dot Product: Dot product or inner product is an algebraic operation that takes two equal-length sequences of numbers and returns a single number.
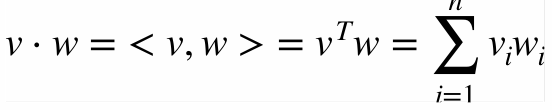
- Unit Vector: Vector with a length of 1.
- Matrix: With m,n ∈ ℕ , a real-valued (m,n) matrix A is a m x n-tuple of elements which is ordered according to a rectangle scheme consisting of m rows and n columns.
- Diagonal Matrix: In $\mathbb{R}^{n \times n}$ the diagonal matrix is defined as a $nxn$ matrix containing numbers on the diagonal and 0 elsewhere.
- Triangular Matrix: A triangular matrix is a square matrix with all entries either above or below the main diagonal being zero
- Identity Matrix: In $\mathbb{R}^{n \times n}$ the identity matrix is defined as a $nxn$ matrix containing 1 on the diagonal and 0 elsewhere.
- Symmetric Matrix: A matrix where the elements are mirrored around the diagonal.
- Gaussian Elimination: Performing elementary transformation to bring a system of linear equations into reduced row-echelon form.
- Span: Span of a space is defined as all possible linear combinations of all the vectors in that space.